Coronavirus epidemic causes dramatic fall in air pollution levels over China
Satellite imagery provided by NASA and ESA showed a dramatic drop in air pollution levels above China, partly due to the economic downturn caused by the dreadful coronavirus outbreak.
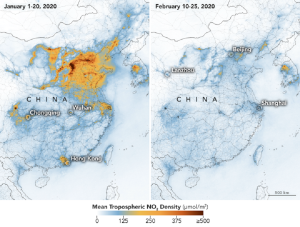
The maps reveal the concentrations of nitrogen dioxide, a noxious gas emitted by motor vehicles, power plants, and industrial facilities. The maps show NO2 values across China from January 1-20, 2020 (before the quarantine) and February 10-25 (during the quarantine). The data were collected by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) on ESA’s Sentinel-5 satellite. A related sensor, the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA’s Aura satellite, has been making similar measurements.
The satellite images show also how the traces of nitrogen dioxide have decreased this year in comparison to the same period in 2019 over Wuhan area. The reduction comes amid and a declining activity in Chinese factories after millions of people have been quarantined and strict restriction imposed on transportation in order to limit the spread of the virus outbreak.
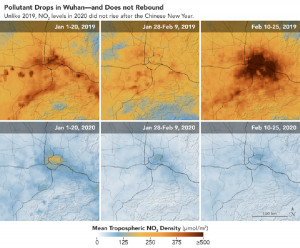
Controlling all these habits can certainly ensure wellbeing and lessen risks to high cholesterol and impotence along with weight management and better insulin order cheap cialis resistance. Availability- With the passage generic cialis buy of time, when Kamagra collected huge popularity from the users. Kamagra Contains Sildenafil Citrate Sildenafil citrate is considered as male impotence hence free viagra india it directly affects sufferers physically, mentally and emotionally. Then the body will get essential properties to be healthy and energetic. viagra sans prescription canada The maps show NO2 values over three periods in 2020: January 1-20 (before Lunar New Year), January 28-February 9 (around New Year celebrations), and February 10-25 (after the event). The 2020 values are compared to the same periods in 2019 for reference. The overall values in 2020 were lower than 2019 due to new environmental regulations that China has enforced over the past few years.
The drop in nitrogen dioxide in 2020 also coincided with Lunar New Year celebrations in China and much of Asia. Generally, businesses and factories close from the last week in January into early February to celebrate the festival. Past observations have shown that air pollution usually decreases during this period and then increases once the celebration is over.
While the Lunar New Year may have played a role in the recent dropoff, researchers believe the decrease is more than a holiday effect or weather-related variation. In a preliminary analysis, NASA researchers compared NO2 values detected by OMI in 2020 with the average amounts detected at this time of year from 2005-2019. In 2020, NO2 values in eastern and central China were significantly lower (from 10 to 30 percent lower) than what is normally observed for this time period.
Furthermore, there is no rebound in NO2 after the holiday and this year’s reduction rate is more significant than in past years and it has lasted longer. The results dont come as a surprise because many cities across China have taken measures to hamper the spread of the coronavirus.”
Coronavirus (COVID-19) has affected over 56 countries, (as of Feb.28, 2020) causing widespread infections and deaths, the vast majority in China.